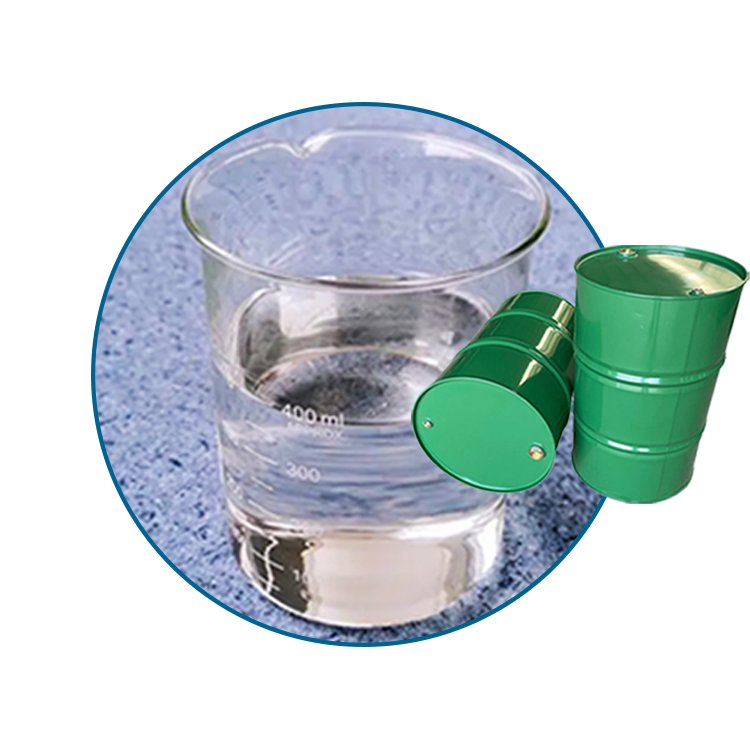
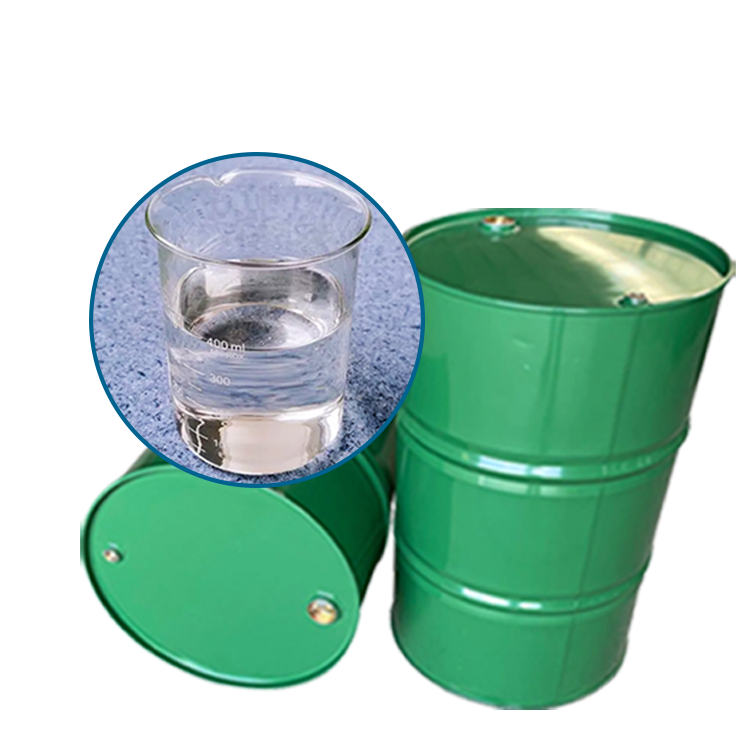
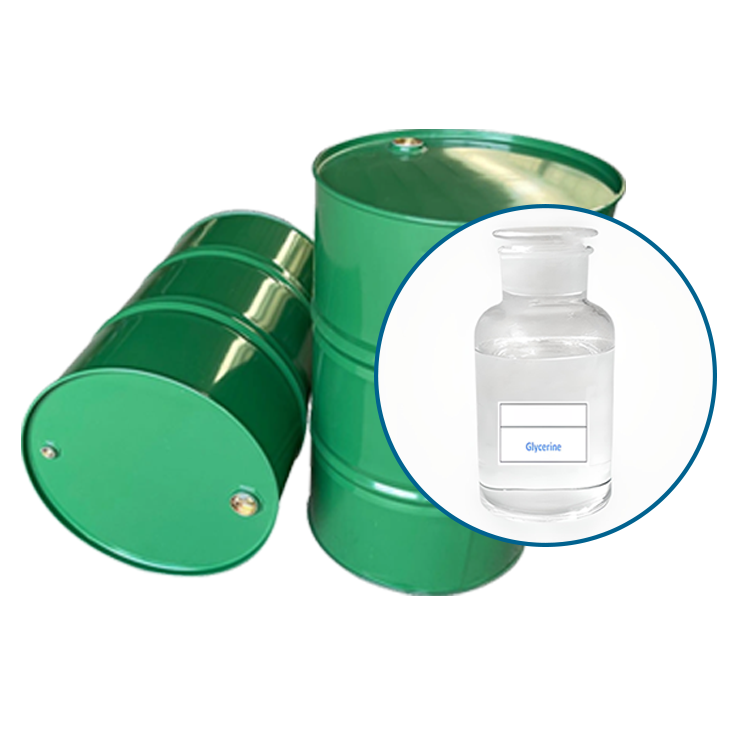
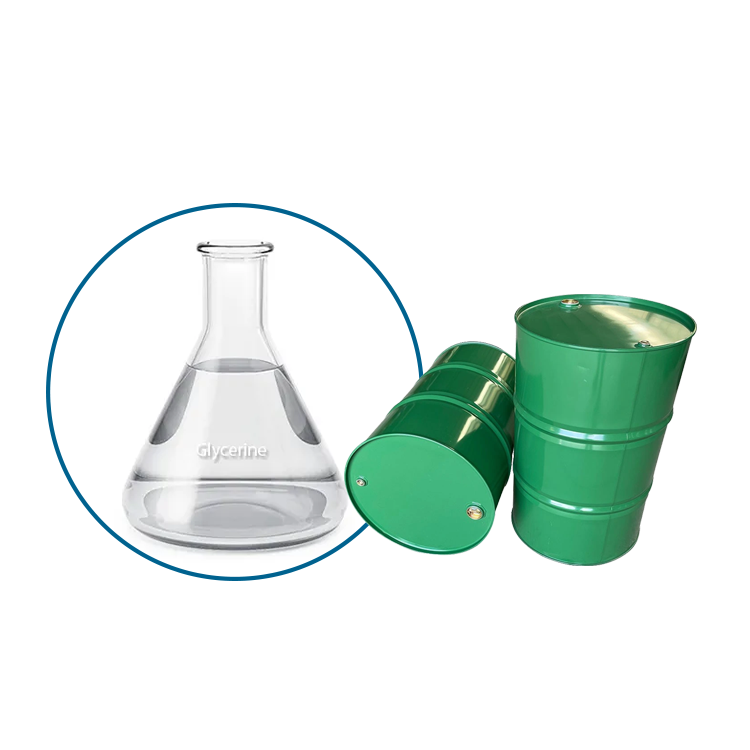
Grease SeriesGlycerine
1.Colorless, transparent, odorless, viscous liquid, sweet taste, with hygroscopicity. With water and alcohols, amines, phenols in any proportion miscible, aqueous solution is neutral. Soluble in 11 times ethyl acetate, about 500 times ether. Insoluble in benzene, chloroform, carbon tetrachloride, carbon disulfide, petroleum ether, oil, long chain fatty alcohol. Combustible, chromium dioxide, potassium chlorate and other strong oxidants can cause combustion and explosion. It is also a good solvent for many inorganic salts and gases. Non-corrosive to metals, can be oxidized to acrolein when used as a solvent.
2. Chemical properties: Esterification with acid, such as esterification with phthalate to produce alkyd resin. Transesterification reaction with ester. It reacts with hydrogen chloride to form chlorinated alcohols. There are two ways to dehydrate glycerol: intermolecular dehydration to produce diglycerol and polyglycerol; Acrolein is obtained by intramolecular dehydration. Glycerol reacts with a base to form alcohols. React with aldehydes and ketones to produce acetals and ketones. Glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone were oxidized by dilute nitric acid. Formic acid and formaldehyde are produced by periodate oxidation. Contact with strong oxidants such as chromic anhydride, potassium chlorate or potassium permanganate can cause combustion or explosion. Glycerol can also be nitrated and acetylated.
3. Non-toxic. Even if the total amount of dilute solution up to 100 g is not harmful, it becomes a nutrient source after hydrolysis and oxidation in the body. In animal experiments, it has the same anesthetic effect as alcohol when consumed in very large quantities.
4. It exists in flue-cured tobacco leaves, burley tobacco leaves, flavored tobacco leaves and flue gas.
5. Naturally occurring in tobacco, beer, wine, cocoa.